Hoshin Kanri for Agile – Toyota’s lean policy deployment translated to Agile – is also an excellent tool to align Squad backlog with their Tribe’s purpose in an Agile organization. In my previous post on Hoshin Kanri for Agile, I introduced an innovative way to apply Hoshin Kanri to align the mission of squads with the purpose of their tribe. But the effect carries on even further: the entire backlog of the squads will remain in line with the mission and purpose. Again, this requires a slightly different use of the principles of Hoshin Kanri.
Agile squads work in sprints. At the end of each sprint, they deliver fully functional solutions for their customers. These solutions should be in line with their mission. And this mission should be in line with their tribe’s purpose. Innovative companies like Spotify use this Agile way of working to continuously deliver improved user experiences. Their product range is relatively simple, and their services are fully digital. But how will this work when traditional companies, banks for instance, transform into digital agile companies? Hoshin Kanri is the right tool for the job.
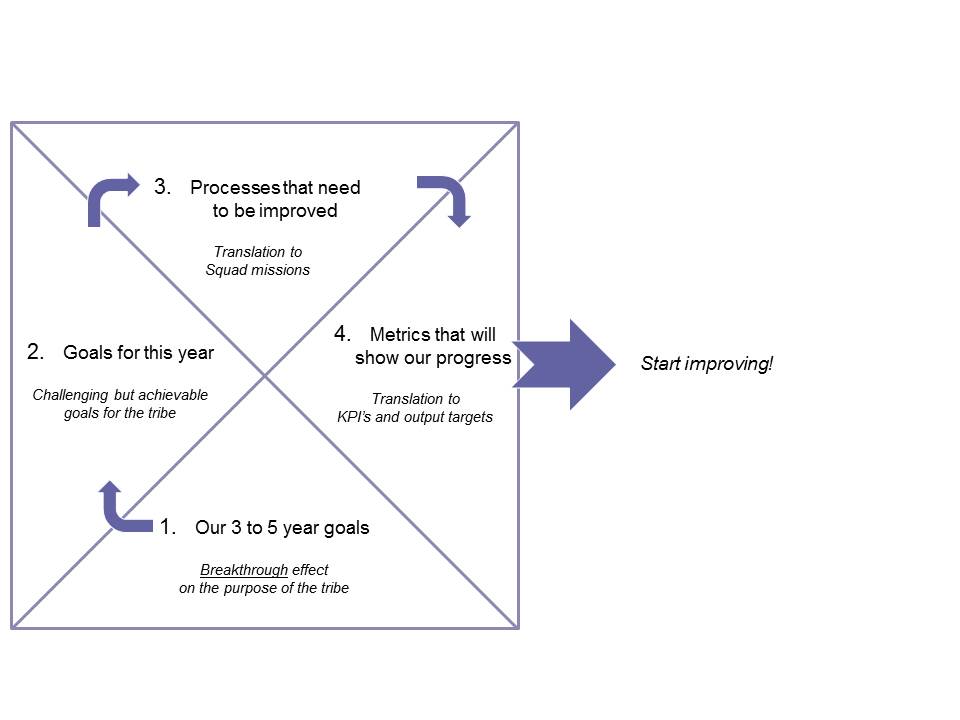
Hoshin Kanri Policy Deployment starts at a strategic level:
- Formulate break-through goals for 3 to 5 years ahead. These are the goals that will make a real impact on the purpose of the tribe.
- Translate these break-through goals into one-year goals. This is the annual plan for the tribe, with challenging but achievable goals.
- Translate these goals to Squad Missions. These missions describe the processes that need to be improved.
- Determine which metrics will show the progress of the improvement.
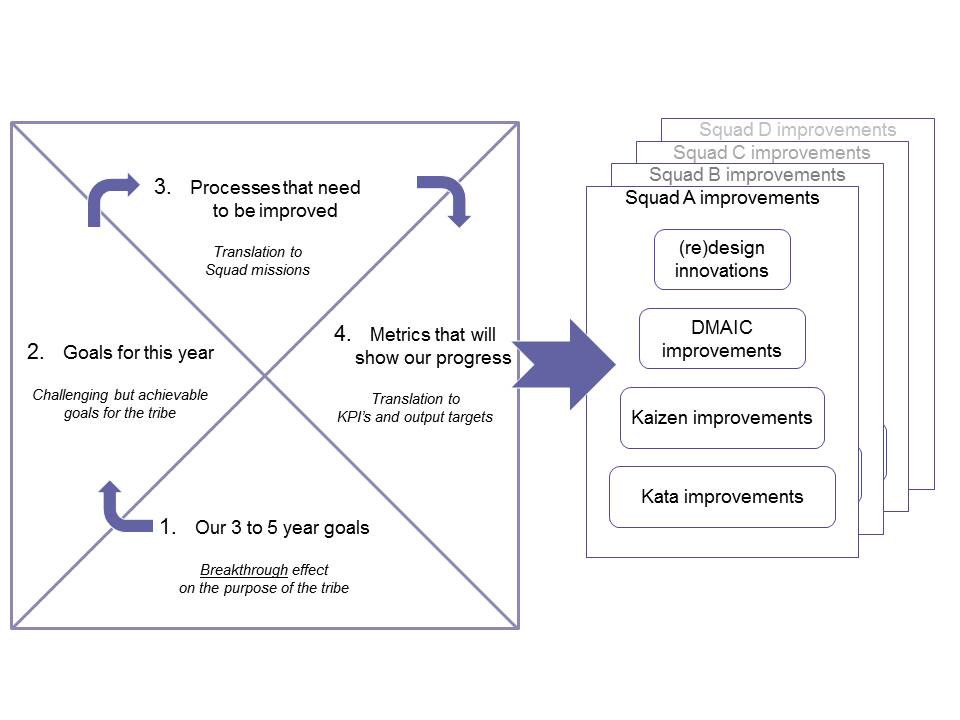
Then, the squad gets to work. But not by creating a backlog directly from their mission. The mission should be used as a starting point for improvements. The squad has a set of proven Lean improvement techniques at their disposal. From large scale to small scale (and from low to high frequency):
- (Re)design, e.g. Value Stream Mapping, Design for Six Sigma or Washing Lanes
- DMAIC projects, executed by green- and blackbelts
- KAIZEN improvements, team improvement sessions
- Kata improvement, weekly improvement as a habit
- Hoshin Kanri for Agile
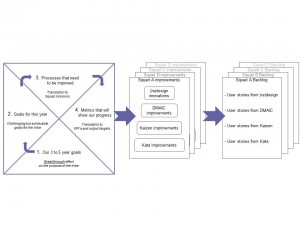
Finally, the backlog is filled from each of these improvements. As each of the improvements are focused on the same strategic priorities, the backlog will be completely in line with mission and purpose.
Menno R. van Dijk